
CBD Molecular Structure 101
Understanding the science behind CBD would better inform you of its potential health benefits. But before we dive into the details, let’s start with the basics. CBD stands for cannabidiol, one of over 100 compounds in the cannabis plant.
Unlike THC, CBD is non-psychoactive, so it won’t make you feel “high” or intoxicated. Although CBD and THC share a similar molecular structure, their atoms are arranged differently. And this subtle difference is why they have very different effects. We have much to cover but don’t worry; we’ll take it slow.
This beginner’s guide will walk you through the molecular details of CBD in an easy, straightforward way. It’s about time you understood the science behind cannabidiol.
Without further ado, let’s get started!
The Chemical Composition of CBD
To understand CBD, you first need to know what it’s made of. CBD is a cannabinoid, a compound found in cannabis sativa plants like hemp. At its core, CBD is composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms.
Its chemical formula, C₂₁H₃₀O₂, represents the precise arrangement of these elements, setting the stage for CBD’s unique properties and therapeutic potential. While seemingly simple, it is within this molecular arrangement that CBD’s true magic resides.
Specifically, cannabidiol CBD has 21 carbon atoms, 30 hydrogen atoms, and 2 oxygen atoms. Carbon makes up CBD’s skeleton, with hydrogen and oxygen atoms attached at different points.
CBD binds to receptors in the brain and body when you ingest CBD. The two main receptors are:
- CB1 receptors – Found mainly in the central nervous system and brain. They affect coordination, mood, thinking, memory, and appetite.
- CB2 receptors – It’s located in the peripheral nervous system and immune cells. And it cures inflammation and pain.
CBD doesn’t bind directly to CB1 and CB2 receptors but influences them indirectly. It helps restore balance in the endocannabinoid system.
All these benefits are thanks to the molecular structure of CBD.
How CBD’s Molecular Structure Gives It Unique Properties
CBD’s molecular structure is pivotal in determining its unique properties and effects on the human body. From treating multiple sclerosis to anorexia, and sleep disorders, CBD has unique healing properties.
Let’s explore how the intricate arrangement of atoms and bonds within CBD gives rise to its exceptional characteristics:
Non-Psychoactive Nature
CBD stands out among cannabinoids for its non-psychoactive properties. Unlike THC, known for its intoxicating effects, CBD does not produce a euphoric “high.” CBD’s molecular structure prevents it from binding firmly to the CB1 receptors in the brain, reducing its psychoactive potential.
Modulation of the Endocannabinoid System (ECS)
The CBD molecular structure we see under a microscope enables it to interact uniquely with the endocannabinoid system (ECS). Rather than directly binding to cannabinoid receptors, CBD modulates their activity.
It inhibits the enzyme FAAH, which breaks down anandamide, an endocannabinoid associated with mood regulation and pain perception. This translates to potential mood-enhancement and pain-relieve effects.
Interaction with Non-Cannabinoid Receptors
Moreover, CBD merges with various non-cannabinoid receptors in the body, expanding its range of effects. For instance, CBD interacts with serotonin receptors, specifically the 5-HT1A receptor regulating mood. Little wonder it’s a great anxiolytic agent that promotes a sense of calm and relaxation.
Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Properties
The molecular structure contributes to its analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. It engages with receptors such as TRPV1 (transient receptor potential vanilloid 1), which is involved in pain perception and inflammation. By activating these receptors, CBD alleviates pain and reduces inflammation. It’s, therefore, helpful in managing conditions like arthritis and neuropathic pain.
Antioxidant Effects
CBD’s structure includes a phenol ring containing a hydroxyl (-OH) group. This confers antioxidant properties to CBD, allowing it to scavenge free radicals and reduce oxidative stress.
CBD may help protect cells and tissues from the harmful effects of free radicals by combating oxidative damage.
Lipophilic Nature
Due to its molecular structure, CBD’s lipophilic (fat-loving) nature influences its solubility and absorption in the body. This property enables it to dissolve in fats and oils. Hence, it’s easily deliverable in various CBD formulations such as oils, tinctures, and topical products. The lipophilic nature also plays a role in its ability to cross cell membranes and reach its target sites within the body.
The Difference Between CBD and THC at a Molecular Level
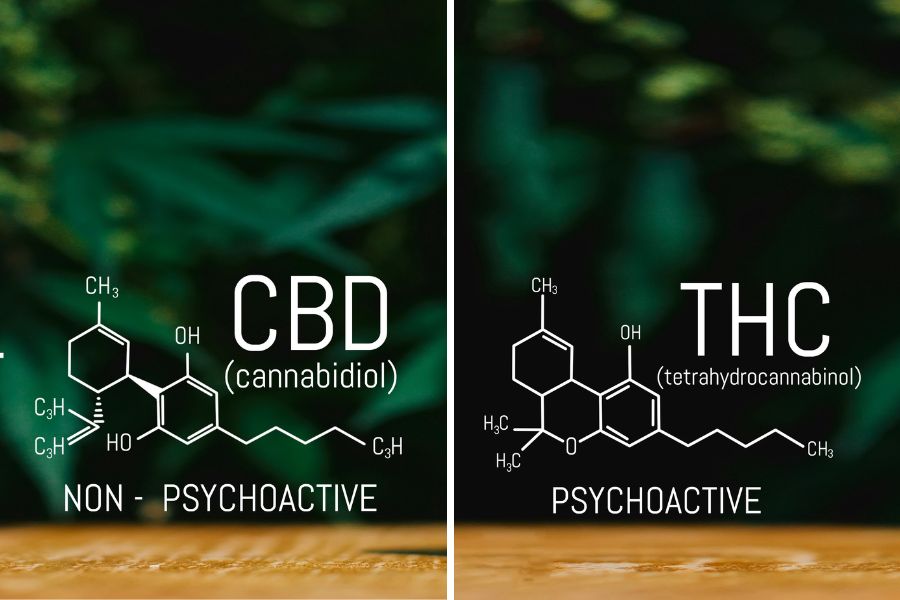
At a molecular level, CBD and THC have key differences that result in very different effects.
Chemical Structure
CBD and THC share the same chemical formula, C21H30O2. But the arrangement of their molecules differs in terms of how the atoms are connected, giving each compound unique properties. Specifically, the position of one double bond in the compounds results in CBD versus THC.
How They Interact with Cannabinoid Receptors
CBD and THC also interact differently with your body’s endocannabinoid system and its cannabinoid receptors, CB1 and CB2.
THC directly binds with CB1 receptors, which are concentrated in the brain and central nervous system. This causes the psychoactive effects or the “high” from marijuana.
In contrast, CBD does not directly bind with CB1 receptors. Instead, it merges indirectly by blocking other compounds that bind with CB1 receptors. CBD also interacts with different receptors in the body linked to pain, mood, and inflammation. This is why CBD does not produce a high and is not psychoactive.
Effects On The Body
Due to their different chemical structures and interactions in the body, CBD and THC also have very other effects:
- THC: pain relief, relaxation, euphoria, impaired memory, and cognition
- CBD Treatment: pain relief, reduced inflammation, improved sleep, decreased anxiety, and potentially help with other conditions like epilepsy. CBD can also help balance out some of the unwanted side effects of THC, like anxiety or rapid heartbeat.
How CBD Interacts With the Endocannabinoid System
CBD works with your endocannabinoid system (ECS), a complex network regulating several essential bodily functions.
The ECS contains endocannabinoids, neurotransmitters that bind to cannabinoid receptors in your brain and immune system.
The Entourage Effect
Cannabidiol also influences other receptors beyond CB1 and CB2. And some of its effects come from its interaction with various compounds in the hemp plant, known as the “entourage effect.”
Full-spectrum CBD products contain all the terpenes, flavonoids, and other cannabinoids found in hemp plants, including trace amounts of THC. These compounds work together synergistically to enhance the benefits of CBD through the entourage effect.
In summary, CBD interacts with your endocannabinoid system and its CB1 and CB2 receptors to maintain balance and homeostasis in the body.
Its influence on this crucial regulatory system gives CBD the potential to provide natural relief for various health conditions.
How CBD’s Molecular Structure Could Lead to New Medical Treatments
CBD’s molecular structure is complex, with many possibilities yet to be explored. As research and clinical trials continue, CBD-rich hemp extracts could lead to promising new treatments.
Anti-inflammatory Effects
Clinical evidence proves that CBD binds with receptors in the endocannabinoid system to regulate inflammation in the body.
Its ability to inhibit chronic inflammation helps conditions like arthritis, irritable bowel disease, and autoimmune disorders. Early research shows CBD applied to the skin could relieve inflammation from eczema and psoriasis.
Neuroprotective Properties
CBD may protect the brain and nervous system from damage due to injury or disease. Its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects slow the progression of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and ALS.
Furthermore, CBD may protect the brain after a stroke or concussion and promote the growth and development of new neurons.
Anxiety and Insomnia Relief
CBD binds with receptors involved in modulating fear, stress, and anxiety. Studies show it may reduce symptoms of PTSD, OCD, panic disorder, and social anxiety.
Pure CBD could improve sleep by reducing anxiety and stress, relaxing the body, and regulating the sleep-wake cycle.
Addiction Management
In addition, it fights addiction by reducing drug cravings and withdrawal symptoms. CBD reduces opioid cravings and anxiety.
While more research is still needed, CBD’s complex molecular structure suggests various therapeutic benefits. As we better understand the endocannabinoid system and CBD’s mechanisms of action, it’s likely to become essential in treating many health conditions. The future of CBD medicine looks extremely promising.
Conclusion
Now that you know CBD inside and out, you’ll have a deeper appreciation for why it interacts with your body the way it does. Pretty cool, right?
Who knew a single molecule could do so much? The next time you take your daily dose of CBD oil or gummies, you can think of all those atoms coming together to bring you relief and balance.
The wonders of chemistry! Consider yourself a CBD molecular structure pro—knowledge is power, after all.


